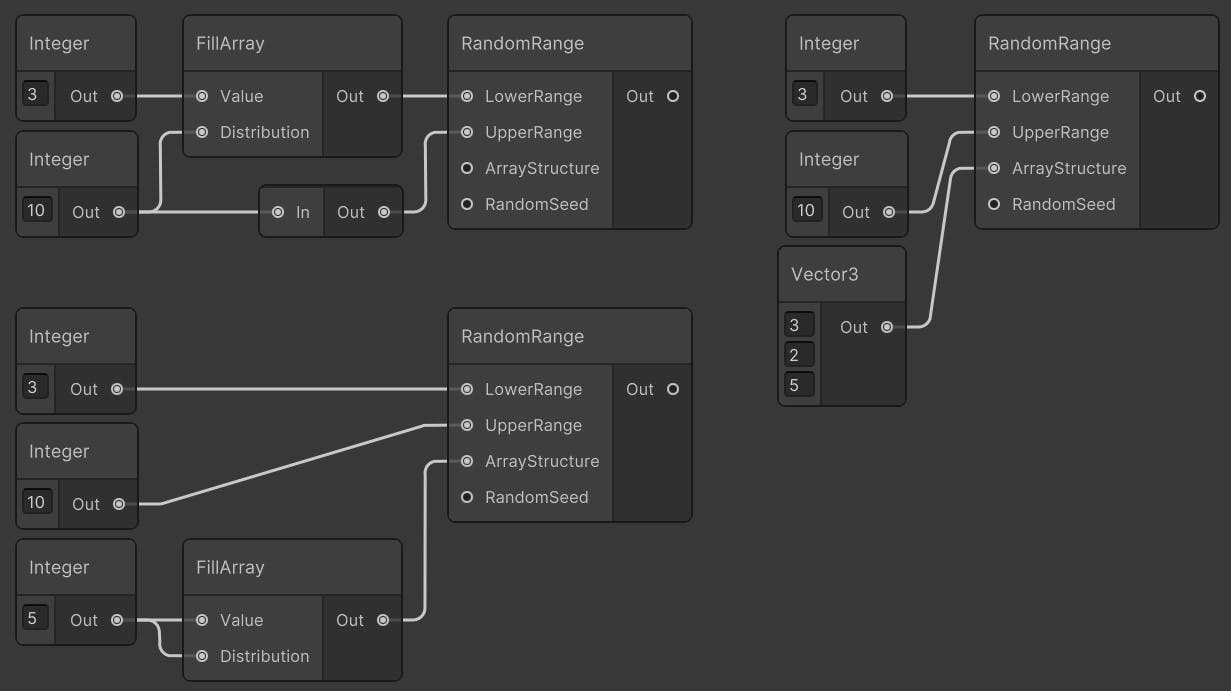
Random Range
Creates an array based on Distribution. Values will be between LowerRange and UpperRange
Inputs
- LowerRange: Lower range of random number (inclusive) (float, int, Vector2, Vector2Int, Vector3, Vector3Int, Vector4)[]-[][]-[][][]-[][][][]
- UpperRange: Upper range of random number (exclusive) (float, int, Vector2, Vector2Int, Vector3, Vector3Int, Vector4)[]-[][]-[][][]-[][][][]
- ArrayStructure: Result array structure. Could be a scalar, if scalar dimensions will be based on its values. (float, int, Vector2, Vector2Int, Vector3, Vector3Int, Vector4)[]-[][]-[][][]-[][][][]
- RandomSeed (optional): Random number generator seed. If not connected, the node will use Graph’s random number generator (int)
Outputs
- Out: Random array based on Distribution port or Lower/UpperRange distribution
Remarks:
Out array distribution is based on either distribution of Lower/UpperRange or Distribution ports. If one of the ranges is a scalar and the other is an array, scalar acts like a same dimension array. If both array, they should be the same dimension. If Distribution port is occupied by a value, Lower/UpperRange should be scalar. If Distribution port is occupied by a scalar such as Vector2, the result will be a T[Vector2.x][Vector2.y] array
Example